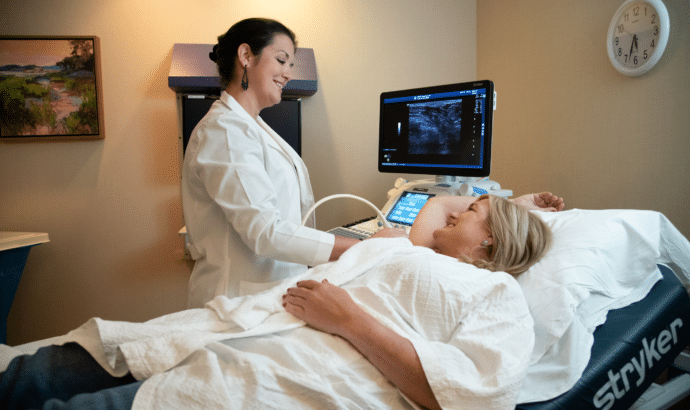
What is an x-ray?
X-rays are generated by an electrical current that passes through an X-ray tube and produces a beam of ionizing radiation that can pass through the body part being examined. This process creates an image of internal body structures called a radiograph.
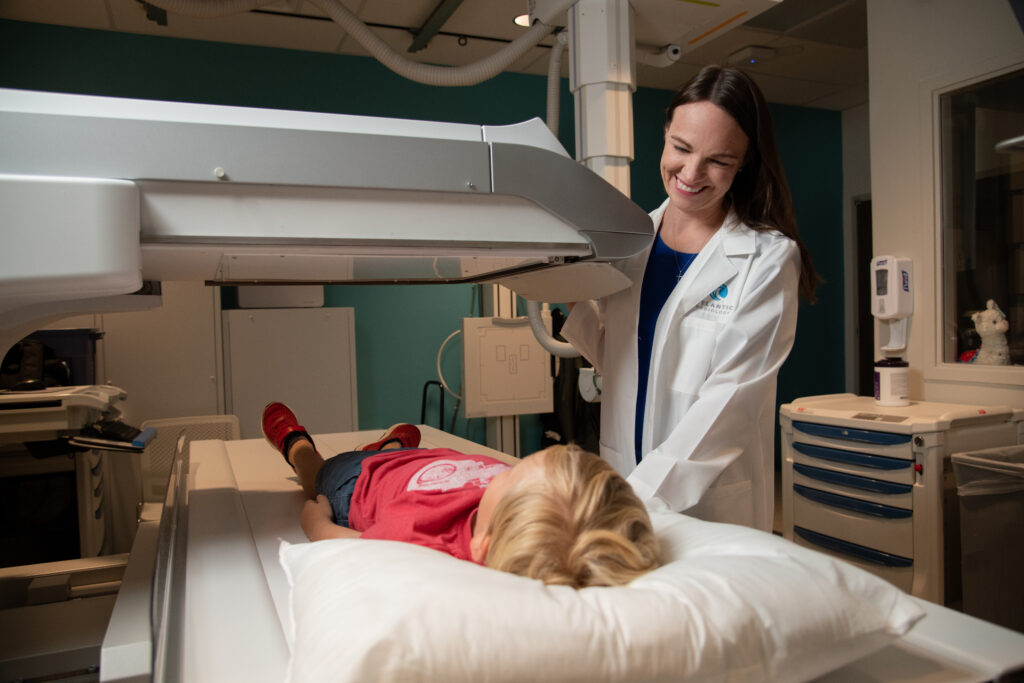
How we perform our X-rays
X-rays are performed on different parts of the body for various diagnostic purposes. A chest X-ray may be performed to look for evidence of pneumonia, tumors, or fluid or to evaluate the size of the heart. X-rays of the abdomen are usually done to determine the cause of acute abdominal pain. They also may be helpful for locating a swallowed foreign object, an intestinal obstruction, or a perforation in the digestive tract. A myelogram is an X-ray of the spine that uses a contrast medium injected into the spinal fluid to outline the spinal cord. It is usually done to check for damaged disks in people with lower back pain. An arthrogram is an X-ray of the inside of a joint (usually the knee or hip) that uses a contrast medium injected into the joint to make the image clearer to detect a tear in the cartilage or other joint abnormality.
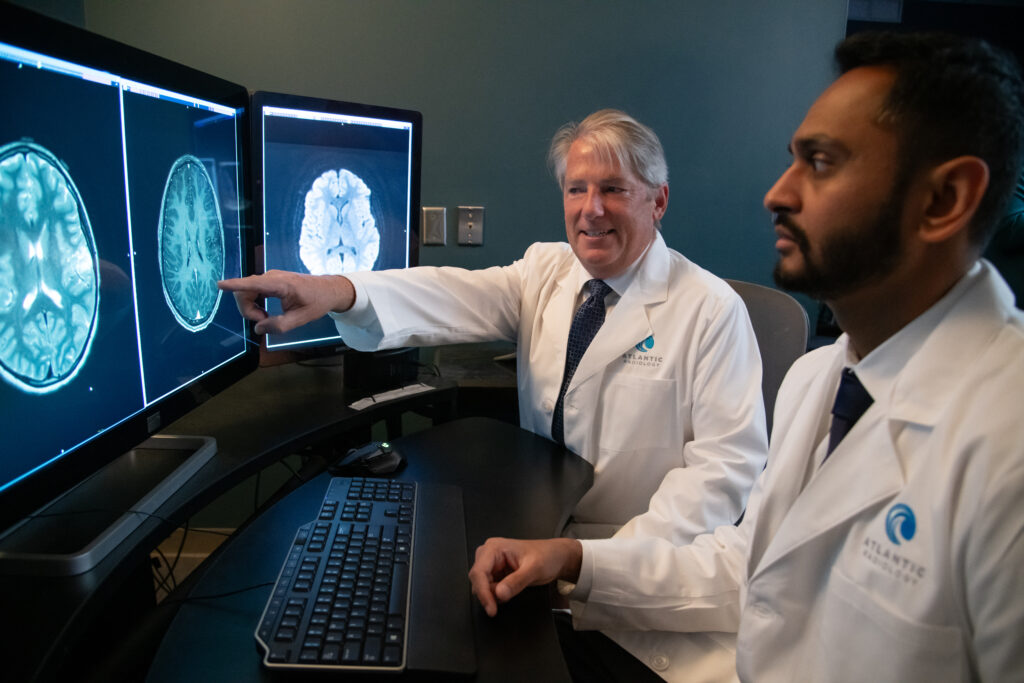
What you will experience during a visit
The person being examined is positioned against a cassette holding the film, or the person may be asked to hold the cassette holding the film against the body part being studied. A lead shield may be placed over other parts of the body to reduce their exposure to the X-rays. The X-ray unit is aligned over the part of the body to be examined. The technician moves away from the area to activate the X-ray unit and to avoid exposing himself or herself to unnecessary radiation. It is important that the person being examined remain as motionless as possible as the X-ray is taken to prevent the images from being blurred. After an X-ray examination, a person can resume normal activities. If a contrast medium was used, it is important that the person consumes extra fluids to enhance the prompt excretion of the contrast medium.
Plain Radiographs can be taken on many body parts.
- Facial Bones including Skull, Jaw, Nasal Bones, Sinuses and Orbits
- Neck
- Chest and Ribs
- Spine-Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar, Sacrum and Coccyx
- Shoulders and Clavicles
- Pelvis and Hips
- Elbows and Knees
- Humerus, Forearm , Wrist and Hands
- Femurs, Lower Legs, Ankles and Feet
- Fingers and Toes
- Abdomen Soft Tissues